Compabloc Free Flow
Alfa Laval Compabloc Free Flow is a highly efficient, fully welded plate heat exchanger, especially developed for use in pharmaceutical applications. It is easy to clean, offers full hygienic properties, exceptional performance, corrosion resistance, and compact size. The result is better product quality and lower operating costs for the customer.
Compact size
Superior heat transfer efficiency in a Compabloc Free Flow makes it possible to reduce the required heat transfer area dramatically compared to an equivalent shell-and-tube or graphite block. This means it can be as small as one-fifth in size compared to a shell-and-tube, and still offer better heat transfer.
The small size is especially valuable if you are planning to increase production but lack space. A Compabloc Free Flow fits anywhere and is easily integrated into your process.
Low costs and long working life
Thanks to the compact size, investment and installation costs for a Compabloc FreeFlow are low, even when the unit is manufactured in highly resistant materials such as Hastelloy.
The robust, fully welded design makes Compabloc Free Flow insensitive to thermal shock and vibrations. It is built for maximum reliability, offers a long working life, and good return on investment.
The high thermal efficiency allows a Compabloc Free Flow to work with a closer temperature approach than a shell-and-tube or graphite block. This makes it possible to use less cooling medium and in some cases a warmer, less costly cooling medium.
Meeting the highest hygienic standards
Compabloc Free Flow has excellent hygienic characteristics. It has no contact points on the product side, is fully drainable, and is easy to clean and inspect. It fully meets the requirements for installation in stringent cGMP processes. The risk of cross-contamination between batches is minimal thanks to the absence of contact points and the crevice-free design, which facilitates fast and thorough cleaning.
Fonctionnement
Condenseur à passage unique
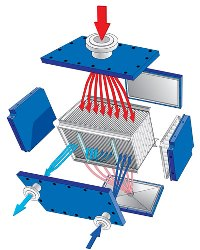
Le condenseur à passage unique convient lorsque la vapeur contient de petites quantités de gaz inertes. La vapeur entre par la grande entrée sur le panneau supérieur et se condense sur les plaques. Le condensat sort par le panneau inférieur incliné et vidangeable.
Condenseur à deux passages
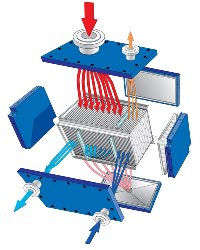
La version à deux passages peut être utilisée lorsque la vapeur contient des fractions plus importantes de gaz inertes. La condensation principale se produit lors du premier passage où la partie condensable de la vapeur se condense sur les plaques avant de sortir par le panneau inférieur inclinable et vidangeable. Les vapeurs non condensables traversent le second passage où elles sont sous-refroidies afin de maximiser la condensation. La turbulence dans le second passage aide à éliminer le brouillard et le vide est facilement aspiré à la sortie du second passage. Avec un condenseur à deux passages, un séparateur de vapeur supplémentaire n'est pas nécessaire, car la séparation a lieu dans l'unité.